Tray dryer: Principle, construction, working, uses, merits and demerits
In the pharmaceutical industry, drying is a crucial process that ensures the stability, efficacy, and longevity of pharmaceutical products. Among the various drying methods, the tray dryer stands out for its simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. Tray dryers are widely used in pharmaceutical engineering to dry a variety of materials, including powders, granules, and wet mass. This article delves into the principle, construction, working, uses, merits, and demerits of tray dryers, highlighting their significance in pharmaceutical engineering.
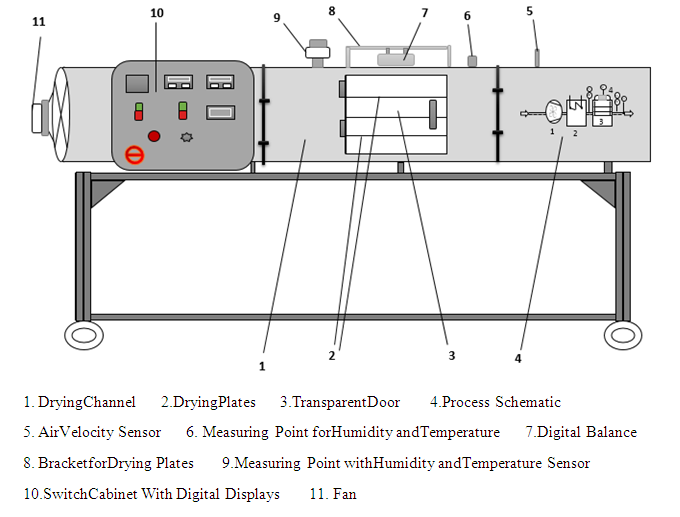
Principle of Tray Dryer
The fundamental principle behind the operation of a tray dryer is convection drying. Convection drying involves the transfer of heat from a hot air stream to the material being dried. The hot air, generated by electric heaters or steam coils, is circulated through the trays containing the material. As the hot air passes over the material, it absorbs moisture, which is then carried away by the air stream. This process continues until the desired level of dryness is achieved.
Construction of Tray Dryer
A tray dryer consists of several key components:
- Chamber: The main body of the tray dryer is a rectangular chamber made from a rigid frame, typically constructed from angle iron. The chamber is double-walled and insulated with high-quality materials such as compressed fiberglass to minimize heat loss.
- Trays: The trays, usually made of stainless steel or aluminum, are placed inside the chamber. They are designed to hold the material in thin layers, ensuring efficient and uniform drying. The number of trays can vary depending on the size of the dryer, ranging from a few trays in laboratory-scale dryers to over 25 trays in industrial-scale dryers.
- Heating System: The heating system consists of electric heaters or steam coils that generate the hot air required for drying. In some models, steam is used as the heating medium due to its cost-effectiveness and energy efficiency.
- Air Circulation System: Fans or blowers are installed to ensure uniform distribution of the heated air throughout the chamber. Direction vanes are placed in the corners of the chamber to direct the airflow along the desired path.
- Control System: The control system includes thermostats and controllers that regulate the temperature and drying time, ensuring precise control over the drying process.
- Insulation: The chamber is insulated to prevent heat loss and improve energy efficiency. This is crucial for maintaining consistent drying conditions and reducing operational costs.
Working of Tray Dryer
The working of a tray dryer involves several steps:
- Loading: The material to be dried is evenly spread on the trays. The trays are then placed inside the drying chamber.
- Heating: The heating system raises the temperature of the air, which is then circulated through the chamber by the fans or blowers.
- Drying: As the hot air passes over the trays, it absorbs moisture from the material. The moisture-laden air is then expelled from the chamber, and fresh, heated air is introduced to continue the drying process.
- Monitoring: The control system continuously monitors the temperature and drying time, making adjustments as needed to ensure optimal drying conditions.
- Unloading: Once the desired level of dryness is achieved, the trays are removed from the chamber, and the dried material is collected.
Uses of Tray Dryer
Tray dryers are used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, chemicals, and agriculture. In the pharmaceutical industry, they are particularly useful for:
Drying Powders and Granules: Tray dryers are ideal for drying powders and granules, which are commonly used in the production of tablets and capsules.
Drying Wet Mass: Wet mass, such as granulated material, can be efficiently dried in a tray dryer to achieve the desired moisture content.
Drying Heat-Sensitive Materials: Tray dryers can be used to dry heat-sensitive materials at lower temperatures, preventing thermal degradation.
Drying Sticky and Viscous Materials: Materials that are sticky or viscous can be spread thinly on the trays, allowing for efficient drying without clumping.
Merits of Tray Dryer
Tray dryers offer several advantages:
- Uniform Drying: The design of the trays and the efficient air circulation system ensure uniform drying across all trays, resulting in consistent product quality.
- Versatility: Tray dryers can handle a wide range of materials, including powders, granules, wet mass, and heat-sensitive substances.
- Batch Processing: Tray dryers are suitable for batch processing, making them ideal for small to medium-scale production with intermittent drying requirements.
- Control: The temperature and drying time can be precisely controlled, allowing for customization of the drying process based on the specific requirements of the material.
- Energy Efficiency: The insulated chamber and efficient heating system minimize heat loss, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
Demerits of Tray Dryer
Despite their advantages, tray dryers also have some limitations:
- Batch Limitations: Tray dryers are not suitable for continuous production, limiting their use in large-scale industries that require continuous drying processes.
- Labor-Intensive: Loading and unloading the trays can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, especially in large-scale operations.
- Energy Consumption: While tray dryers are energy-efficient compared to some other drying methods, they may still have higher energy consumption compared to more advanced drying technologies.
- Space Requirements: Tray dryers can occupy significant floor space, which may be a limitation in facilities with limited space.
Conclusion
Tray dryers play a vital role in pharmaceutical engineering, providing an efficient and versatile solution for drying a wide range of materials. Their ability to ensure uniform drying, handle various materials, and offer precise control over the drying process makes them an essential tool in the pharmaceutical industry. However, their limitations, such as batch processing and labor-intensive operation, must be considered when selecting a drying method. By understanding the principle, construction, working, uses, merits, and demerits of tray dryers, pharmaceutical engineers can optimize the drying process to achieve high-quality, stable, and effective pharmaceutical products. As technology advances, further innovations in drying methods and equipment will continue to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the drying process in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Frequently asked questions
What is a Tray Dryer?
Answer: A tray dryer is a conventional drying equipment used in the pharmaceutical industry to remove moisture from materials such as powders, granules, and other substances. It consists of a heated chamber with multiple trays stacked on top of each other, where the drying process occurs under controlled temperature and humidity conditions.
How Does a Tray Dryer Work?
Answer: A tray dryer works on the principle of convection drying. Hot air generated by electric heaters or steam is circulated through the perforated trays containing the material to be dried. The hot air removes moisture from the material, and the moist air is expelled from the chamber. This process ensures uniform drying of the material.
What Are the Advantages of Using a Tray Dryer?
Answer: Tray dryers offer several advantages, including cost-effectiveness, simplicity of operation, and suitability for drying a wide range of materials. They are also energy-efficient and can achieve uniform drying, making them ideal for large-scale pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
What Are the Applications of Tray Dryers in Pharmaceutical Engineering?
Answer: Tray dryers are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for drying sticky materials, plastic substances, granular masses, crystalline materials, precipitates, and pastes. They are essential for producing high-quality pharmaceutical products by ensuring the removal of moisture to achieve the desired consistency and stability.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us
