Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)
Ischemic heart disease is an acute or chronic cardiac disability caused by imbalance between the myocardial oxygen demand and supply of oxygenated blood. The term coronary artery disease is alternatively used for ischemic heart disease. Cardiac function is largely depended on continuous flow of oxygenated blood through the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries supply oxygen to myocytes and removes waste product like carbon dioxide, lactic acid and hydrogen ions.
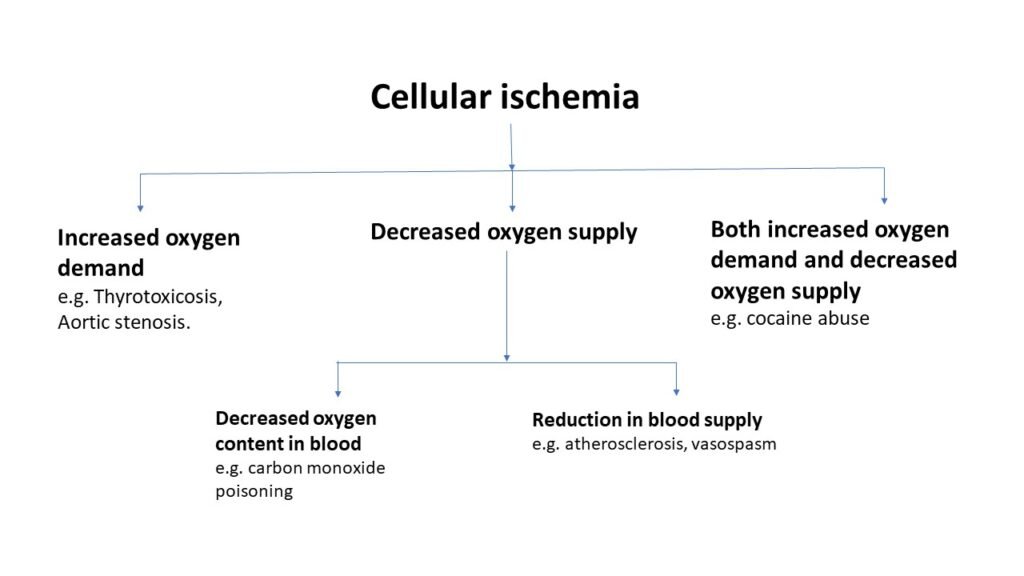
Ischemic heart disease occurs due to one of the following reasons;
- Increased oxygen demand
- Decreased in oxygen supply
- Combination of both, increased oxygen demand and decreased oxygen supply
Decreased oxygen supply is the main cause seen at clinical level, particularly due to atherosclerotic disease. Cocaine abuse decreases oxygen demand along with reduction in blood supply, hence causes ischemic effect.
Etiology
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is mainly caused by coronary artery diseases (mostly atherosclerosis). Atherosclerosis causes constant obstruction in the coronary artery. More than 75% reduction in diameter of coronary artery may lead to chronic ischemic condition. Various atherosclerotic complications like calcification, haemorrhage, rupture, thrombosis may worsen the condition.
There may be other non-atherosclerotic reason like vasospasm, thrombus formation, embolism, coronary stenosis. These reasons are seen in about 10% cases of ischemic heart disease (IHD).
Silent ischemic heart disease (IHD)
Ischemic episodes may be common within the people, who are unaware of them. This condition is known as silent ischemic heart disease (IHD). Silent ischemic episodes may go undiagnosed in angina patients. They can suddenly get heart attack. Diabetes patients or patients having history of heart attack are vulnerable to developing silent ischemic heart disease (IHD).
Symptoms of Ischemic heart disease (IHD)
The most common symptom of ischemic heart disease (IHD) is angina pectoris. There is chest pain similar to indigestion or heart burn. Other symptoms may include;
- Chest discomfort, chest pain, heaviness, tightness that spreads to arms and back, shortness of breath, pressure.
- Stomach gas or indigestion
- Increased work rat, usually when exercising
- Clammy skin
- Nausea with or without vomiting
- Dizziness or fainting
Risk factors of ischemic heart disease (IHD)
There are various factors that increase the chances of developing ischemic heart disease (IHD). Risk factors include;
- Family history of heart disease
- High cholesterol or triglycerides
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking and other tobacco use
- Sleep apnea
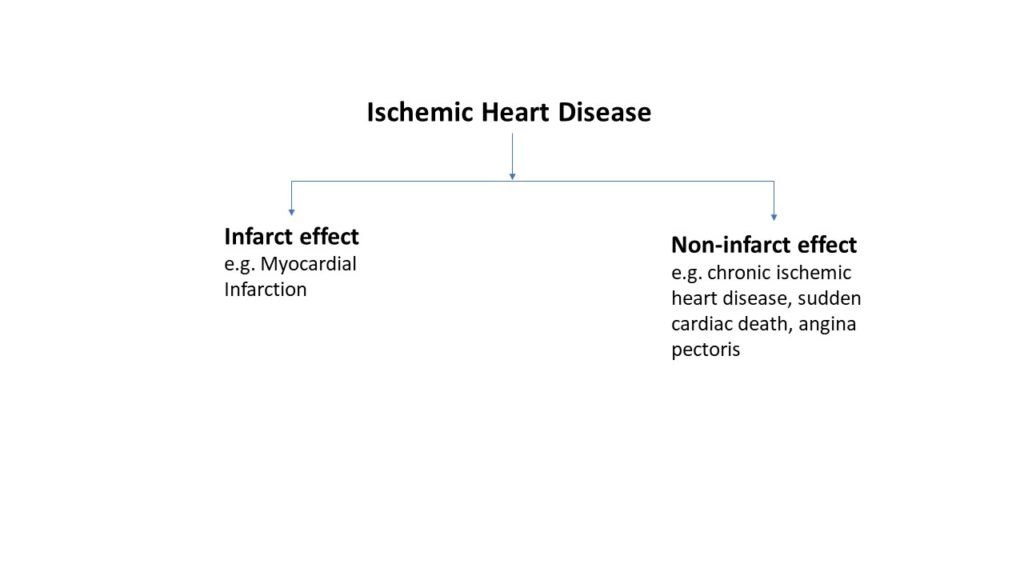
Types of ischemic heart disease (IHD)
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) can be classified as infarct effect and non-infarct effect. Infarct type include myocardial infarction (MI) while non-infarct includes angina pectoris, sudden cardiac death and chronic heart disease.
Treatment for ischemic heart disease (IHD)
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) can be treated by one of the following approach;
- Lifestyle management
- Pharmacotherapy
- Surgery
Lifestyle management
The risk of developing ischemic heart disease (IHD) can be minimised by improving lifestyle. Some of the healthy lifestyle changes are as follows;
- Engaging in regular physical activity, which lowers cholesterol to optimum level
- Keeping blood pressure in control
- Stopping addiction of tobacco products, alcohol.
- Avoid unhealthy foods in diet like, junk foods, oily foods, etc.
Pharmacotherapy
There are various drugs of different classes used in the treatment of ischemic heart disease (IHD).
- Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors): Eg. Enalapril, lisinopril, perindopril, ramipril. Etc
- Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs): Eg. Telmisartan, olmesartan, valsartan, azilsartan, losartan, etc.
- Anti-ischemic medicines: Eg. Ranolazine, nitro-glycerine, etc.
- Antiplatelet medication: Eg. Aspirin, clopidogrel, etc.
- Beta blockers: Eg. Atenolol, metoprolol, propranolol, etc.
- Statins: Eg. Atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin, etc.
- Calcium channel blockers: Eg. Amlodipine, nifedipine, etc.
Procedures to manage ischemic heart disease (IHD)
If medications are alone are insufficient to relieve symptoms of ischemic heart disease (IHD), surgeries like coronary angioplasty, stent replacement or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) are advised. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) and stent replacement is a catheter-based procedure to remove plaque and restore blood flow in clogged arteries.
Summary
Ischemic heart disease (IHD), commonly known as coronary artery disease, is a medical condition characterised by reduced blood flow to the heart muscles. The primary cause is mostly the accumulation of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) in the coronary arteries leading to narrowed or blocked vessels.
The main symptoms of ischemic heart disease (IHD) are chest pain, typically triggered by physical or emotional stress. In severe cases a complete blockage of coronary artery can result in heart attack. Risk factors of ischemic heart disease (IHD) include, smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol and sedentary lifestyle. Medical interventions include medicines to manage risk factors and in severe cases procedures like angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Frequently asked questions
What is ischemic heart disease (IHD)?
Ischemic heart disease (IHD), commonly known as coronary artery disease, is a medical condition characterised by reduced blood flow to the heart muscles.
What causes ischemic heart disease (IHD)?
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) occurs when blood flow to the myocardium (heart muscles) is obstructed by partial or complete blockage of coronary artery.
What are the risk factors for ischemic heart disease (IHD)?
Risk factors of ischemic heart disease (IHD) include, smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol and sedentary lifestyle.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us
