Introduction
Prescription is written order from registered medical practioner, or other properly licenced practitioners to a pharmacist to compound and dispense a specific medication for the patient. Prescription writing stands as a cornerstone in the practice of medicine, serving as the crucial link between healthcare providers and patients access to appropriate mediations. In this article we will see prescription, parts of prescription, types of preparations, Latin words used in prescription, handling of prescription and errors in prescription.
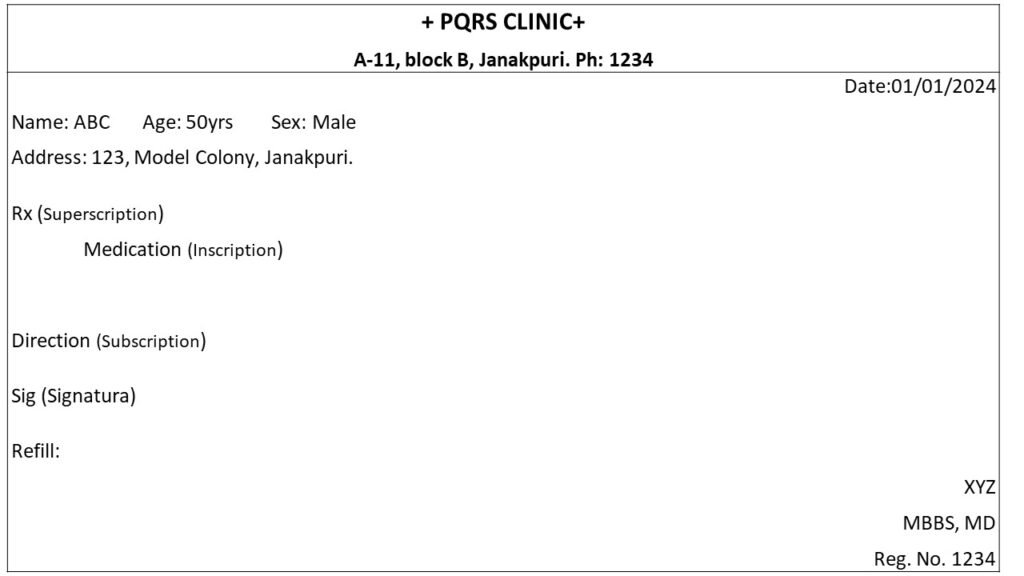
Parts of a prescription
- Date
- Name, age, sex and address of the patient
- Superscription
- Inscription
- Subscription
- Signatura
- Renewal instruction
- Signature, address and registration number of the prescriber.
- Date: It helps the pharmacist to avoid the misused of prescription by patient of habit-forming drugs.
- Name, age, sex and address of patient: It help the pharmacist to calculate the appropriate dose of medication.
- Superscription: It is represented by a symbol Rx which written before writing the prescription. It is an abbreviation of the Latin word recipe, meaning You Take.
- Inscription: this is the main part of the prescription. It contains the names and quantities of the prescribed ingredients.
- Subscription: This comprises the direction to the pharmacist for preparing the prescription.
- Signatura: This consists of the direction to be given to the patient regarding administration of the drug. Usually written as Sig in prescription.
- Renewal Instructions: It indicates whether prescription may be renewed or not.
- Signature, address and registration number of the prescriber: It contains the signature of the prescriber along with its registration no. and address.
Sample Prescription
Latin terms and abbreviation commonly used in prescription
Type of dosage forms
| Latin term | Abbreviation | Meaning in English |
| Auristille | Auristill | Ear drop |
| Capsula | Caps | A capsule |
| Charta | chart | A powder |
| Collutotium | Collut | A mouth wash |
| Collirium | Collyr | An eye wash |
| Cremor | Crem | A cream |
| Emulsio | Emul | An emulsion |
| Haustus | Ht | A drought |
| Injectis | Inj | An injection |
| Linctus | Lin | A linctus |
| Linimentum | Lin | A liniment |
| Liquor | Liq | A solution |
| Lotio | Lot | A lotion |
| Naristillae | Narist | Nasal drops |
| Nebula | Neb | A spray solution |
| Pasta | Past | A paste |
| Pilula | Pil | A pill |
| Pulvis | Pulv | Powder |
| Solutio | Sol | A solution |
| Suppositorium | Suppose | A suppository |
| Tabela | Tab | A tablet |
| Unguentum | Ung | An ointment |
Time of administration
| Semel in die | sem in die | Once a day |
| Bis in die | b.i.d., b.d. | Twice a day |
| Ter in die | t.i.d., t.d. | Three times a day |
| Quarter in die | q.i.d., q.d. | Four times a day |
| Sexies in die | sex.i.d. | Six times a day |
| Anti cibos | a.c. | Before meals |
| Post cibos | p.c. | After meals |
| Inter cibos | i.c. | Between meals |
| Modedicto | m.d. | As directed |
| Si opus sit | s.o.s. | When necessary |
| Statim | stat. | Immediately |
Handling of a prescription
Handling of a prescription refers to the process a pharmacist follows when a patient presents a prescription. It typically involves the following steps.
- Receiving: The pharmacist should personally receive the prescription. While receiving a prescription from a patient, a pharmacist should maintain a neutral facial expression.
- Reading and Checking: The prescription should be read and checked for legality, legibility, completeness, and correctness. This includes checking the physician’s details, patient’s details, and product details.
- Collecting and Weighing the Material: All the materials required for the prescription should be collected from the shelves or drawers and kept on the left-hand side of the balance. After measuring each material, it should be kept on the right-hand side of the balance.
- Compounding, Labelling, and Packaging: Only one prescription should be compounded at a time. Compounding should be done on a clean table. All equipment required should be cleaned and dried.
Errors in prescription
Prescription errors are preventable events that may cause inappropriate medication use or patient harm. Here are some common types of prescription errors.
- Abbreviation: Abbreviated terms used by the prescriber can lead to major errors during interpretation by the pharmacists.
- Name of the Drugs: Names of some drugs, especially the brand names, either look or sound alike. So, any error in the name of a drug can lead to major danger to the patient.
- Strength of the Preparation: Drugs are available in the market in various strengths. A drug must not be dispensed if the strength is not written in the prescription.
- Dosage Form of the Drug Prescribed: Many drugs are available in more than one dosage form e.g. liquid, tablets, injections, or suppositories. The dosage form intended for the patient must be mentioned in the prescription to reduce ambiguity.
- Dose: If an unusually high or low dose is mentioned in the prescription then it must be consulted with the prescriber.
- Instructions to the Patient: Sometimes the instruction for a certain preparation is either omitted or mentioned partially. The quantity of the drug to be taken, the frequency and timing of administration, and the route of administration should be mentioned clearly.
- Incompatibilities: It is essential to check that there are no pharmaceutical or therapeutic incompatibilities in the prescription.
Summary
A prescription is a formal communication from a physician or registered medical practioner to a pharmacist, authorizing them to dispense a specific prescription drug for a specific patient. There are four parts of prescription. The first is superscription, meaning to take. The second part is inscription, which specify the ingredients and their quantities. The third part is the subscription, which tells the pharmacist how to compound the medicine. The fourth and last part is the signatura, in which healthcare provider indicates what instructions are to be put on the outside of the package to tell patient when and how to take the medicine and in what quantities.
Frequently asked question
What do you mean by the prescription?
Prescription is written order from a registered medical practioner, or other properly licenced practitioners to a pharmacist to compound and dispense a specific medication for the patient.
What are the parts of prescription?
- Date
- Name, age, sex and address of the patient
- Superscription
- Inscription
- Subscription
- Signatura
- Renewal instruction
- Signature, address and registration number of the prescriber.
What is the meaning of Rx in prescription?
Rx is a symbol used as an abbreviation for recipe and was commonly placed at the beginning of a prescription to instruct the pharmacist or patient to take certain ingredients or medicines.
What are OTC drugs?
Over-the-counter (OTC) medicines are those that can be sold directly to people without a prescription. OTC medicines treat a variety of illness and their symptoms including pain, coughs and colds, diarrhoea, constipation, acne and others.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us

2 thoughts on “Prescription”