Principle, Construction, Working, Uses, Merits and Demerits of Elutriation Tank 
In the pharmaceutical industry, the separation and classification of particles are crucial for ensuring the quality and efficacy of products. One of the effective methods used for this purpose is the elutriation tank. Elutriation tanks are designed to separate particles based on their size and density using a fluid medium, typically air or water. This blog will delve into the principle, construction, working, uses, merits, and demerits of the elutriation tank, providing a comprehensive overview for professionals and enthusiasts in the field.
Principle of Elutriation Tank
The elutriation tank operates on the principle of fluid dynamics and gravity separation. The key principles include:
- Fluid Dynamics: The elutriation tank utilizes an upward flow of fluid to carry particles of varying sizes. The fluid flow creates a drag force that acts on the particles.
- Gravity Separation: Heavier particles settle faster in the fluid due to gravity, while lighter particles remain suspended or settle more slowly. This difference in settling velocities allows for the separation of particles based on size and density.
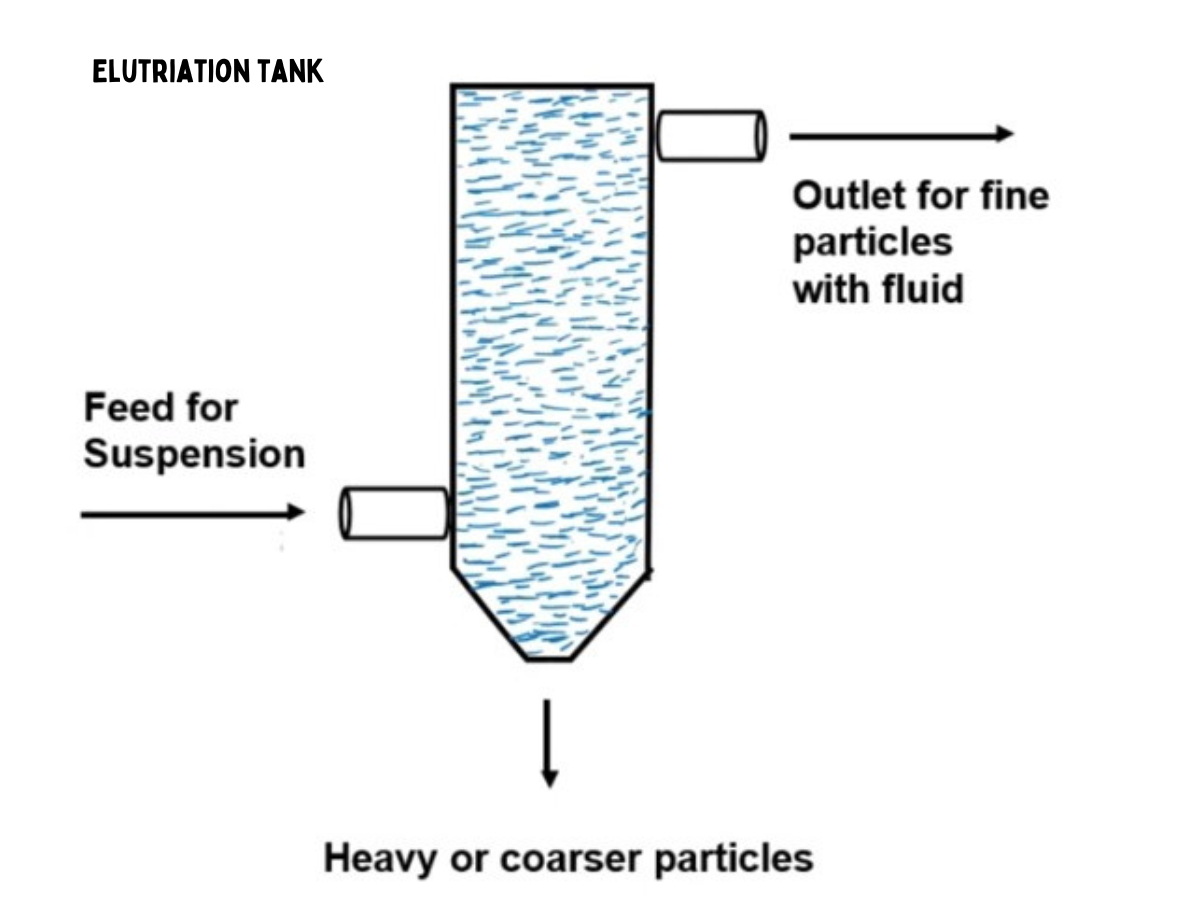
Construction of Elutriation Tank
The construction of an elutriation tank typically includes the following components:
- Tank Structure: A vertically oriented tank with an inlet for introducing the fluid and a bottom outlet for collecting separated particles.
- Inlet System: Designed to introduce the fluid, creating an upward flow that entrains particles.
- Outlet System: Located at the bottom to collect settled particles.
- Particle Collection System: May include a system for collecting particles at various heights to separate them based on settling velocity.
Working of Elutriation Tank
The working process of an elutriation tank involves the following steps:
- Introduction of Fluid: Fluid, often air or water, is introduced into the elutriation tank.
- Particle Suspension: As the fluid flows upward, it entrains particles, keeping them in suspension.
- Settling: Heavier particles settle faster due to gravity, and lighter particles remain suspended or settle more slowly.
- Separation: Particles are separated based on their settling velocities, with faster-settling particles collected at lower points in the tank.
- Collection: Separated particles are collected at different heights or at the bottom of the tank.
Uses of Elutriation Tank
Elutriation tanks are used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and mineral processing. In the pharmaceutical industry, they are used for:
- Particle Size Classification: Commonly used for classifying particles based on size in industries such as mineral processing and particle research.
- Density Separation: Employed for density-based separation, particularly in the processing of minerals and ores.
- Particle Characterization: Utilized in laboratories for characterizing particles based on their settling behavior.
- Seed Sorting: Applied in agriculture for sorting seeds based on size and density.
Merits of Elutriation Tank
- High Precision: It provides a high level of precision in separating particles based on size and density.
- Continuous Operation: Can operate continuously, facilitating the separation of large quantities of particles.
- Gentle Separation: The process is relatively gentle on particles, making it suitable for fragile or easily damaged materials.
- Adaptable: Can be adapted for various particle sizes and densities by adjusting fluid flow rates.
Demerits of Elutriation Tank
- Complex Setup: Elutriation systems can be complex to set up and may require careful calibration.
- Limited to Size and Density: Primarily applicable for size and density separation and may not be effective for other types of particle characteristics.
- Energy Consumption: Depending on the scale and design, it may consume significant energy.
Conclusion
The elutriation tank is an indispensable tool in the pharmaceutical industry, offering efficient and versatile particle separation capabilities. Understanding its principle, working, uses, merits, and demerits is crucial for optimizing its performance and ensuring the production of high-quality pharmaceutical products. By leveraging the benefits of the tank while addressing its limitations, pharmaceutical professionals can enhance their manufacturing processes and contribute to the advancement of pharmaceutical sciences.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us