Introduction
Cell is the smallest functional unit of the human body. Individual cells are very tiny in nature and cannot be seen with naked eyes. A group of cell comes together and forms a tissue. Each tissue has some specialized function. For example, blood, bone, muscle, etc. A group of tissues having similar function is called as organ for example, heart, liver, intestines, lungs, etc. These organs come together to form a system like digestive system, respiratory system, reproductive system, etc. Each system has its own particular function which maintains homeostasis and contributes to health of human. In this article we will see the cell, structure and function of cell.
Structure and function of cell
The cell cannot be seen with naked eyes but it can be observed under a microscope using various stains. Human cell consist of plasma membrane in which number of cell organelles are present. Inside plasma membrane there is watery fluid called as cytosol. Organelles are the small structures with highly specialised function. They include nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, microfilaments and microtubules.
Plasma membrane
It is a biological membrane which separates and protects the interior of cell from extracellular space. Plasma membrane consists of two layers of fatty substances containing phospholipids. It also contains protein molecules embedded in membrane. The phospholipid molecule has a tail like structure with round shaped head at one end. The head is electrically charged and hydrophilic in nature. The tail has no charge (neutral) and hydrophobic in nature. The phospholipid bilayer us arrange like sandwich with hydrophilic heads aligned on outer surface of membrane and hydrophobic tails forming central water repelling layer.
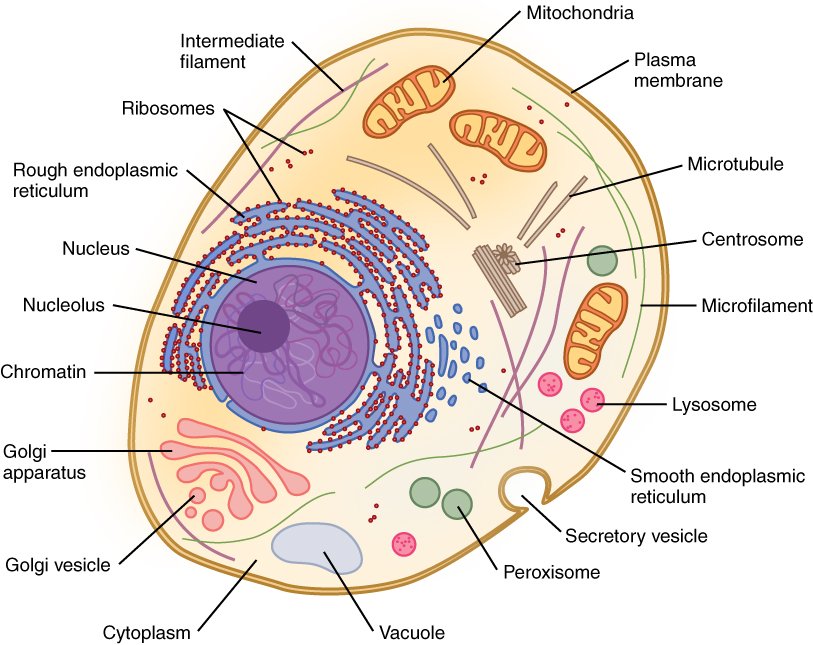
Nucleus
Nucleus is the central unit of cell. It controls every activity which happens in cell. Some cells do not contain nucleus like mature erythrocytes. It is surrounded by a membrane called as nuclear membrane. It is the largest organelle and embedded in the cytoplasm. Nucleus contain the body’s genetic material, which is responsible for activities of the cell. This genetic material is made up of DNA and histone proteins, which are coiled together to form a network of threads called as chromatin fibre. During cell division these chromatin fibres becomes more tightly coiled to form chromosomes.
The functional sub unit of chromosome is called as gene. Each cell contains a part of gene which is appropriate to the cells own specialised function. The enzymes required for metabolic processes of body are synthesized only if the controlling gene is present. This concept is called as ‘one gene, one enzyme’. If a particular gene is missing, the body can not produce associated enzyme and certain metabolism does not occur. There are number of diseases caused by such inborn error of metabolism. for example, phenylketonuria, abnormal haemoglobin and some immune deficiency.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria is the sausage shaped structure present in cytoplasm, which is surrounded by double unit membrane. Mitochondria is involved in aerobic respiration in which chemical energy is made available in the cell. The energy is stored in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which releases energy after the breakdown of cell. The mitochondria are also known as ‘power house of cell’.
Ribosomes
These are tiny granules composed of RNA and protein. They are present as free units or in small clusters in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes synthesize proteins from amino acids using RNA as the template. They are found on outer surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Endoplasmic reticulum is the series of interconnecting membranous canals present in the cytoplasm. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum, smooth ER and rough ER.
- Smooth ER: It synthesises lipids and steroid hormones. It is also associated with detoxification of some drugs.
- Rough ER: It contains ribosomes on its surface. These are the sites of synthesis of proteins like enzymes and hormones.
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus consist of closely folded flat membranous sacs. It is present in more quantity in cells which synthesise and export proteins. The proteins are stored in the Golgi apparatus into the membrane bound vesicles called as secretory granules.
Lysosomes
These are the secretory vesicles formed by Golgi apparatus. They contain enzymes required for breakdown of organelles and large molecules, for recycling or excretion as waste material. In WBC lysosomes contain enzymes which digest foreign material like microbes.
Microfilaments
Microfilaments are the tiny strands of protein which provides structural support and maintain the characteristic shape of the cell.
Microtubule
Microtubule are the contractile protein structures present in the cytoplasm. They are involved in movement of the cell and cell organelles within the cell.
Summary
Cells are the basic units of life. They have a complex structure with various cell organelles, each one serving specific functions. The cell membrane covers the cell, controlling the passage of substances. Nucleus contains the genetic material of cell while endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria plays an important role in synthesis, processing and energy production. Cells are of different types which adapt to specific functions in multicellular organisms. Understanding the cell structure and function is crucial for comprehending life processes and biological systems.
Frequently asked questions
Which cell does not contain nucleus?
Red blood cells (RBCs) do not contain nucleus.
What are 2 types of ER?
The 2 types of endoplasmic reticulum are smooth ER and rough ER.
What is the difference between smooth and rough ER?
The main difference between smooth and rough ER is the presence of ribosome. The ribosome is present in rough ER while it is absent in smooth ER.
What is called as power house of cell?
Mitochondria stores the chemical energy in the form of ATP hence they are called as power house of cell.
Who discovered Golgi apparatus?
Camillo Golgi discovered Golgi apparatus in 1898.
What is the function of nucleus?
The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle which contains the genetic material required for cellular processes. The nucleus control and regulate the activities of the cell.
For more regular updates you can visit our social media accounts,
Instagram: Follow us
Facebook: Follow us
WhatsApp: Join us
Telegram: Join us

1 thought on “Structure and Function of Cell”